Here are five facts about how the world’s population is projected to change by the end of the century, based on Pew Research Center analysis of the United Nations’ World Population Prospects
(The latest data is from 2023, so the numbers for 2024 and beyond are projections.)
#1
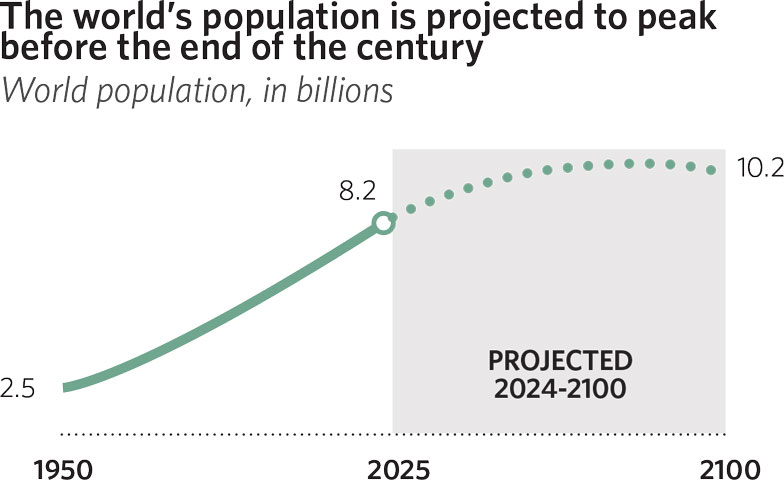
Although the world’s population more than tripled in the last 75 years, the U.N. expects it to grow by only about 1.9 billion between now and 2100 (from some 8.2 billion to 10.2 billion).
#2
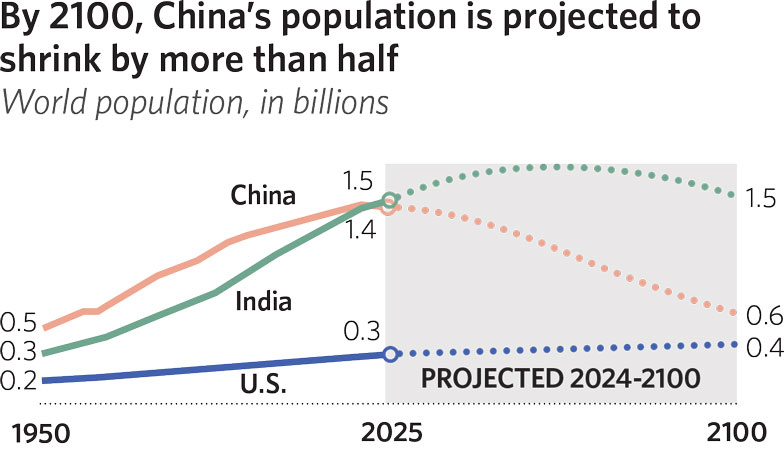
The world’s three most populous countries are expected to have different trajectories over the century: India is projected to peak at 1.7 billion people and then decline to 1.5 billion by 2100. China’s population is expected to drop to 633 million. The U.S. is expected to grow slowly and steadily to 421 million.
#3
Five countries are expected to contribute to more than 60% of the world’s population growth by 2100: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Pakistan, and Tanzania. Among the 10 countries projected to contribute most to global population growth, the U.S. is the only one located outside of Africa and Asia. Still, the U.S. is expected to fall from the world’s third-most populous country today to the sixth-most populous by 2100.
#4
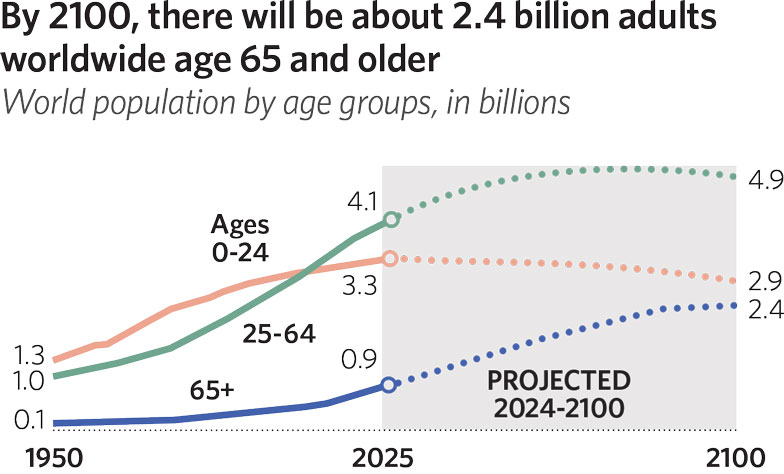
The world’s population is expected to get older. The world’s median age is projected to rise to 42 by 2100, up from 31 today and 22 in 1950.
#5
Africa is the world’s youngest region and is projected to stay that way by the end of the century. The median age in Africa is 19, which is expected to rise to 35 by 2100. Europe is the oldest region, with a median age of 43.